[Measure & Optimize]
You are provided with the javascript code to track the activity on the page
-> Sends relevant data to GA to be measured
SDK: Software Development Kit
Easy to integrate
-> for Android/ iOS
Google Tag Manager: easy to control and implement different google tags(i.e. GA tags, Google AdWords tag, Double Click tags and so on)
Basic Principles in Google Analytics
1) collection
2) processing
3) configuration: filters
4) reporting: google analytics interface
Thursday, March 29, 2018
Saturday, March 24, 2018
[Display Advertising] 05. Video Advertising
Importance of Video Ad
- On average, US adults spend 1 hour and 8 mins per day watching online video(YouTube platform)
VIdeo + Content Marketing strategy
- Creative possibilities
- Video consumption is an important part of the mobile experience
- Online video offers powerful targeting
- Often part of a larger content strategy
Online video ads: types and formats
1. Instream vs. Outstream Video Ads
- Instream video ads:
These are video ads that are played before (pre-roll ad), during (mid-roll ad) or after (post-roll ad) a video. These ads typically cannot be stopped from playing. In some cases the user can skip the ads after a few seconds.In some cases, a group of ads will play subsequently. Such a group is sometimes referred to as an Ad Pod.
- Outstream video ads:
These are video ads that take place outside of the in-line video experiences. There are several types of outstream ads:
- Native Video: Video ads integrated into the format of a website. These ads typically include a headline, a description, and context for the ad. (ex, on Yahoo website...etc.)
- In-article Video: Video ad that plays between paragraphs of editorial text content (within the article)
- In-feed Video: A native video ad in a social feed (e.g. Twitter), often paired with a headline, description and logo (ex, Twitter)
- Interstitial: Video that appears between two content pages (sometimes also referred to as a transition ad, an intermercial ad or a splash page)
Autoplay vs. Interactive Video Ads
- Autoplay Video Ads: Video ad starts playing without any user interaction
- Interactive Video Ads: Video ads that respond to user input. That input could be starting, pausing or stopping the ad. But it can also be other actions like clicking, filling out a poll inside the video, etc. The interaction is meant to engage the user more with the ad.
Long Form vs. Short Form Video
- When we talk about long or short form video, we refer to the video the ads are being showed in.
- Long Form Video: Longer pieces of video content (more than 10 mins), typically telling a full story (e.g., movies, original series, etc.).
- Short Form Video: Video with a duration of less than 10 mins.
Vertical Video
- While most video plays in landscape orientation, with the orientation of a typical mobile phone device, videos in portrait orientation have become more popular. Vertical Video refers to video that displays in portrait format, no matter how it was shot initially. (ex, Snapchat)
Video Ad Platforms
Tips for effective video ad online
1. Target your ads to your audience: sophisticated targeting is the hallmark of online advertising
2. Create high quality video: make sure your video puts your product or your message in a good light
3. Focus on the beginning of the video: because users can skip the video after a few secs
4. Make your ad work without audio: in many video platforms, ads will start playing without user interaction but also without audio(until the user interacts).
5. Use short video ads: users have little patience for ads, especailly when they are consuming short form video conetnt. Keep your ads short - research shows that 15 sec video ads perform well online. Shorter ads (e.g. the 6 second bumper ad on YouTube) are becoming popular as well.
6. Choose the tone of the ad based on your objective: You can use different tones to bring your message across in a video ad. You use humor, emotion or you can keep things informational
7. Include a call to action: add a button users can click where you can provide a call to action. Or, include a URL or a reference to your FB page for instance, to make sure users know how to follow up on your msg.
Google Ad Words Video Ad Formats
True View video ads: You're only charged when viewers watch or interact with elements of your video.
- It's a win-win: Viewers see videos they're curious about, and you get more views from an audience you know is interested. Because you choose what you want to pay for a view, you get the right audience at the right price. Unlike cost-per-impression (CPM) pricing, you won't need to pay every time your ad is shown.
- Freedom to customize: You can also run videos longer than 30 seconds, so you can experiment with different formats. You can try longer product demos, customer testimonials, or a how-to video demonstrating your product in action.
- Broad reach: TrueView ads can appear on both YouTube and other publisher sites in the Display Network for desktop computers and high-end mobile devices. Note that video content for TrueView ads must be hosted on YouTube.
TrueView in-stream ads:
When should I use it? Use this format when you have video content you'd like to promote before other videos on YouTube and across the Google Display Network.
How does it work? Your video ad plays before, during, or after other videos.
Where can the ads appear? TrueView in-stream video ads can appear on YouTube watch pages and on videos on partner sites and apps in the Display Network.
How will I be charged? You pay when a viewer watches 30 seconds of your video (or the duration if it's shorter than 30 seconds) or interacts with your video, whichever comes first.
TrueView video discovery ads (this format is formerly known as “TrueView in-display ads.”):
When should I use it? Use this format to promote a video in places of discovery, including next to related YouTube videos, as part of a YouTube search result, or alongside other content across the Display Network.
How does it work? Your ad consists of a thumbnail image from your video with some text. While the exact size and appearance of the ad may vary depending on where it appears, video discovery ads always invite people to click to watch the video. The video then plays on the YouTube Watch page or on your channel page.
Where can the ads appear? On YouTube search results; Alongside related; YouTube videos; On the YouTube homepage; As an overlay on a YouTube watch page; On video partner sites and apps across the Display Network
How will I be charged? You’ll be charged only when viewers choose to watch your ad by clicking the thumbnail.
Bumper ads are a short video ad format designed to allow you reach more customers and increase awareness about your brand.
When should I use it? Use this format when you’d like to reach viewers broadly with a short, memorable message.
How does it work? Your bumper video ad is 6 seconds or shorter and plays before, during, or after another video. Viewers do not have the option to skip the ad.
Where can the ads appear? Bumper ads can appear before other videos on YouTube or on partner sites and apps on the Display Network.
How will I be charged? You pay based on impressions. Bumper ads use CPM (cost-per-thousand impressions) bidding, so you pay each time your ad is shown 1,000 times.
Youtube Director App can help you create video ads on a small budget
Two tactics to use are:
* Video Advertising Glossary:
http://dvglossary.www2.iab.com/#block-block-1
- On average, US adults spend 1 hour and 8 mins per day watching online video(YouTube platform)
VIdeo + Content Marketing strategy
- Creative possibilities
- convey emotions
- rich imagery
- tell stories
- Video consumption is an important part of the mobile experience
- Online video offers powerful targeting
- Often part of a larger content strategy
Online video ads: types and formats
1. Instream vs. Outstream Video Ads
- Instream video ads:
These are video ads that are played before (pre-roll ad), during (mid-roll ad) or after (post-roll ad) a video. These ads typically cannot be stopped from playing. In some cases the user can skip the ads after a few seconds.In some cases, a group of ads will play subsequently. Such a group is sometimes referred to as an Ad Pod.
- Outstream video ads:
These are video ads that take place outside of the in-line video experiences. There are several types of outstream ads:
- Native Video: Video ads integrated into the format of a website. These ads typically include a headline, a description, and context for the ad. (ex, on Yahoo website...etc.)
- In-article Video: Video ad that plays between paragraphs of editorial text content (within the article)
- In-feed Video: A native video ad in a social feed (e.g. Twitter), often paired with a headline, description and logo (ex, Twitter)
- Interstitial: Video that appears between two content pages (sometimes also referred to as a transition ad, an intermercial ad or a splash page)
Autoplay vs. Interactive Video Ads
- Autoplay Video Ads: Video ad starts playing without any user interaction
- Interactive Video Ads: Video ads that respond to user input. That input could be starting, pausing or stopping the ad. But it can also be other actions like clicking, filling out a poll inside the video, etc. The interaction is meant to engage the user more with the ad.
Long Form vs. Short Form Video
- When we talk about long or short form video, we refer to the video the ads are being showed in.
- Long Form Video: Longer pieces of video content (more than 10 mins), typically telling a full story (e.g., movies, original series, etc.).
- Short Form Video: Video with a duration of less than 10 mins.
Vertical Video
- While most video plays in landscape orientation, with the orientation of a typical mobile phone device, videos in portrait orientation have become more popular. Vertical Video refers to video that displays in portrait format, no matter how it was shot initially. (ex, Snapchat)
Video Ad Platforms
Tips for effective video ad online
1. Target your ads to your audience: sophisticated targeting is the hallmark of online advertising
2. Create high quality video: make sure your video puts your product or your message in a good light
3. Focus on the beginning of the video: because users can skip the video after a few secs
4. Make your ad work without audio: in many video platforms, ads will start playing without user interaction but also without audio(until the user interacts).
5. Use short video ads: users have little patience for ads, especailly when they are consuming short form video conetnt. Keep your ads short - research shows that 15 sec video ads perform well online. Shorter ads (e.g. the 6 second bumper ad on YouTube) are becoming popular as well.
6. Choose the tone of the ad based on your objective: You can use different tones to bring your message across in a video ad. You use humor, emotion or you can keep things informational
7. Include a call to action: add a button users can click where you can provide a call to action. Or, include a URL or a reference to your FB page for instance, to make sure users know how to follow up on your msg.
Google Ad Words Video Ad Formats
True View video ads: You're only charged when viewers watch or interact with elements of your video.
- It's a win-win: Viewers see videos they're curious about, and you get more views from an audience you know is interested. Because you choose what you want to pay for a view, you get the right audience at the right price. Unlike cost-per-impression (CPM) pricing, you won't need to pay every time your ad is shown.
- Freedom to customize: You can also run videos longer than 30 seconds, so you can experiment with different formats. You can try longer product demos, customer testimonials, or a how-to video demonstrating your product in action.
- Broad reach: TrueView ads can appear on both YouTube and other publisher sites in the Display Network for desktop computers and high-end mobile devices. Note that video content for TrueView ads must be hosted on YouTube.
TrueView in-stream ads:
When should I use it? Use this format when you have video content you'd like to promote before other videos on YouTube and across the Google Display Network.
How does it work? Your video ad plays before, during, or after other videos.
Where can the ads appear? TrueView in-stream video ads can appear on YouTube watch pages and on videos on partner sites and apps in the Display Network.
How will I be charged? You pay when a viewer watches 30 seconds of your video (or the duration if it's shorter than 30 seconds) or interacts with your video, whichever comes first.
TrueView video discovery ads (this format is formerly known as “TrueView in-display ads.”):
When should I use it? Use this format to promote a video in places of discovery, including next to related YouTube videos, as part of a YouTube search result, or alongside other content across the Display Network.
How does it work? Your ad consists of a thumbnail image from your video with some text. While the exact size and appearance of the ad may vary depending on where it appears, video discovery ads always invite people to click to watch the video. The video then plays on the YouTube Watch page or on your channel page.
Where can the ads appear? On YouTube search results; Alongside related; YouTube videos; On the YouTube homepage; As an overlay on a YouTube watch page; On video partner sites and apps across the Display Network
How will I be charged? You’ll be charged only when viewers choose to watch your ad by clicking the thumbnail.
Bumper ads are a short video ad format designed to allow you reach more customers and increase awareness about your brand.
When should I use it? Use this format when you’d like to reach viewers broadly with a short, memorable message.
How does it work? Your bumper video ad is 6 seconds or shorter and plays before, during, or after another video. Viewers do not have the option to skip the ad.
Where can the ads appear? Bumper ads can appear before other videos on YouTube or on partner sites and apps on the Display Network.
How will I be charged? You pay based on impressions. Bumper ads use CPM (cost-per-thousand impressions) bidding, so you pay each time your ad is shown 1,000 times.
Youtube Director App can help you create video ads on a small budget
Two tactics to use are:
- Pause keywords with high CPC cost
- Expand the list of keywords with keywords similar to the best performing keywords
* Video Advertising Glossary:
http://dvglossary.www2.iab.com/#block-block-1
[Display Advertising] 04. Display Ad with Google AdWords

Types of ads:
- search ads
- display ads
- video ads
- app ads: mobile app installation advertising for Android
Steps for setting up your display campaign:
1. Articulate your marketing objective
2 Set your budget
- The Campaign Spent < Expected Profit
3. Target your campaign
4. Create your ad
5. Measure and optimize
Contextual targeting: match relevant site content
- Content keywords: Choose words and phrases relevant to your products and services.
- Topics: Similar to keywords, this lets you place your AdWords ads on website pages about the topics that you choose.
- Audiences: Reach specified groups of people
Ad Formats in Google Adwords
Responsive ads are ads that automatically adjust their size, appearance, and format to fit available ad space. Most of the ads have images, but they could also adjust to just show text.
2. Dynamic Ads
Rich media ads that match people’s location and the content they are seeing, delivering a more compelling message.
3. Lightbox Ads
Rich interactive formats to reach, delight and engage customers with imagery and compelling messaging in different sizes and formats adjusted to the available ad space.
4. Video Ads
Non-skippable in-stream video ads (15 secs, sometimes 30 secs) that run in video content of Display Network Partner sites. Note that if you want your entire campaign to be delivered in video, it is better to set it up as a video advertising campaign, which will give you the option to also run your ads on YouTube (which is not possible through the Ad Gallery).
5.General Purpose Ads
Using text and an image, AdWords adds a bit of animation to attract users’ attention.
6. Gmail Ads
Expandable, interactive ads that appear above the promotions tab in Gmail Inboxes.
[Display Advertising] 03. Display Ad Sales Model
[The Changing Sales Model]
Deals Executed
Deals Executed
- Where will ads run?
- Number of impressions
- Start and end date
Ad Networks Emerged: Publisher's Ad Space
remnant unsold ad inventory
sold premium ad inventory
The Different Display Advertising Sales Models
1. Direct(Premium) Advertising
ex) NYTimes, CNN.com, ESPN.com, Yahoo!., and Buzzfeed
- Planned ahead of time
- Preferred by large brand advertisers
- Typically for larger budgets
- Primarily context based targeting
- Pricing is mostly on a CPM(cost per thousand impressions) basis
- More options for customization
- Advertising Operations(Ad Ops):
Once a sale is done, the publisher needs to create what is called an 'Insertion Order'(IO). That is basically how they instruct the ad server to insert the ad in the right content at the right time. The publisher also needs to keep a schedule and manage the sold inventory, and they have to make sure the inventory they sold is actually available.
2. Advertising Networks
- Planned ahead of time
- Different specializations
- In-person or self-serve: Google's Display Advertising Network(Adsense)
- Targeting in Ad Networks: targeting is mostly contextual or demographic, although behavioral targeting and other forms of targeting are also possible
- Pricing primarily CPM
Examples of Ad Networks
Ad networks
- Google Advertising Network (GAN)
- Media.net
- Adcash
- Yahoo! Advertising Network
Mobile Ad Networks
- AdMob
- InMobi
Video Ad Networks
- Youtube
- Tubemogul
- Brightroll (Yahoo!)
3. Ad Exchanges
- Auction-based: ad exchanges offer advertising space from a large no. of publishers and sell it in real time to the highest bidder in an auction
- Advertisers buy individual ad spaces
- Sales happen in real time
- Targeting is primarily behavioral, although other means of targeting are possible
- Intermediaries: the sale is facilitated by intermediaries on both the side of the advertisers(through Demand-Side Platforms - DSPs) and the publishers (through Supply Side Platforms - SSPs)
- Ads are charged on an impression basis(CPM)
-> examples of ad exchanges are the Doubleclick Ad Exchange(owned by Google), OpenX, and Advertising.com, owned by AOL
-> Consider it as a wholesale environment; most ad exchanges don't allow individuals in.
When you choose an exchange to bid in, make sure it is one with plenty of high quality inventory, so you can find the audiences you need.
Programmatic Advertising
- buying "people", not fixed ad space
: buys cookies associated with people so that the ad will be shown to the most relevant audience possible on the website
- impression by impression (not in bulk)
- primarily behavioral targeting
- fully automated:
the exchange between SSP and DSP happens in a millisecond(almost simultaneously) that a person will not recognize that the ad has just been loaded
Parties involved are:
As soon as the user comes to the website, the user profile (data) is passed on to the supply side platform (SSP) who puts up the user’s profile for sale in the exchange. The Demand Side Platform (DSP) compares the user profile to the profiles it is looking for its advertisers, and if the profile is a match, they put in a bid. The highest bidder wins and can show its ad to the user. The auction happens in real-time.
Sunday, March 18, 2018
[Display Advertising] 02. Display Ads and Targeting
Evolution of display advertising
- After the first display banner ad was launched by Wired, display advertising quickly grew to a multi-million dollar business
- The fast growth gave rise to a large no. of different ads of all shapes and sizes
- The IAB(Interactive Advertising Bureau) stepped in to help standardize
- IAB still publishes Ad Standards and Guidelines for different types of digital advertising(www.iab.com)
Display Ads and the Customer Journey
- Display Ads work for different stages in the customer journey
- They are most often used in 'Awareness' stage. Interest and Desire stage
Different Ad Formats
- VPAID (Video Player-Ad Serving Interface Definition)
- Linear Video Ads: More commonly known as pre, mid and post-roll ads, linear ads take over the full video player space. They're linear because they run in line sequentially with the content, for example, a pre-roll will appear as (ad-video); a mid-roll will be (video-ad-video) and a post-roll will appear as (video-ad). Linear ads can be 15 or 30-seconds long and do not allow for fast forwarding through the ad.
- Non-linear Video Ads: These ads run simultaneously with the video content, usually in the form of an interactive banner ad in an overlay. Clicking on these ads pauses the content and the ad opens in a full screen player. Generally, a non-linear video ad will run for 5-15 seconds before rotating to another ad or reducing in size.
- Native Ads: ads that look like the native content from the webpage. They are unlikely to be blocked by AdBlock software and thus is preferred nowadays.
Different Ad Types
- Direct Response Ads
- Typical for the action stage
- Clicks are important
- Advertise specific action such as 'register now for the program' (Click To Action buttons)
- Brand Ads
- Typical for the awareness & interest stage
- Clicks are less important
- Advertise the general brand to raise awareness or shape brand image
Metrics
- # of impressions
- # of unique impressions
- Click Through Rate (CTR)
- no. of clicks/total no. of imp * 100
- Click to Conversion Rate(CTC)
- no. of conversion/ total no. of clicks *100
- Example of conversion could be a purchase
- Engagement/ Interaction Rate: no. of actions taken such as clicks
- View Through Rate (VTR): when a user has finished watching the entire video ad
- View Through Conversion(VTC): Conversion after 30 days after the first impression of the ad
- ROI: Return On Investment
- ROI: profit - total cost
- ROI percentage: (ROI/ total cost) * 100
Pricing Models
Performance-Based Pricing:
Advertiser pays for conversions
Advertiser pays for conversions
- Priced at cost per click(CPC)
- Priced at cost per action(CPA): good for advertisers, bad for publishers
Impression Based Pricing:
Advertiser pays for impressions
- Priced at cost per thousand impressions(CPM)
Reach and frequency concepts
- Reach: the no. of unique people that see your ad
- Frequency: the average no. of times your ad is shown to the same user
Targeting
- Demographic targeting: gender, age, education, income...etc.
- Geographical targeting: location
- Contextual targeting: interest
- Behavioral targeting: users who viewed certain items, stopped at the purchase (Giving nudge -> retargeting ad)
Display Ads in Mobile
- Responsive ad formats for ads in a browser
- In-app advertising: banners and native ads
Display Advertising Concerns
- Ad blocking: Many users using 'AdBlock' software to block ads -> native ads are becoming more popular
- Viewability: ads that are not viewed are checked as 'viewed'. This is problematic as advertisers pay for CPM. Policies to prevent 'ad fraud' is becoming popular.
[Display Advertising] 01. How Display Ads Work
Content and Ad Servers
CMS: Content Management System
ex) word press, blogger ...etc.
Ad Server
1) Publisher Ad Server
2) Advertiser Ad Server
Data and Display Advertising
1. Data in the form of log files
- log files are a record kept in the publisher's server that detail the interactions between the user and a website
2. Data in the form of cookies
- Cookies are stored in the user's browser, they are small text files that are used to connect user behavior within and across sessions, usually by assigning a user ID
- First party cookies are set by the website(first party) a user is visiting
- Third party cookies are set by another party the website(first party) has an agreement with
3. Data in mobile
Data outside the browser environment in mobile captured in Advertiser IDs
- For Android: Android Advertiser ID
- For iOS: IDFA(ID for Advertisers)
Data as the basis for targeting display advertising
- Every online user has a user data profile based on their usage over time. That profile forms the basis for digital advertising targeting
- Digital Data Profile contains cookies, Facebook ID, Google ID, device ID, location
- Publishers use content servers and Content Management System (CMS) to bring content online. Ad servers fill in the advertising space. The publisher's ad server communicates with the advertiser's ad server to make that happen.
CMS: Content Management System
ex) word press, blogger ...etc.
Ad Server
1) Publisher Ad Server
2) Advertiser Ad Server
Data and Display Advertising
1. Data in the form of log files
- log files are a record kept in the publisher's server that detail the interactions between the user and a website
- Cookies are stored in the user's browser, they are small text files that are used to connect user behavior within and across sessions, usually by assigning a user ID
- First party cookies are set by the website(first party) a user is visiting
- Third party cookies are set by another party the website(first party) has an agreement with
3. Data in mobile
Data outside the browser environment in mobile captured in Advertiser IDs
- For Android: Android Advertiser ID
- For iOS: IDFA(ID for Advertisers)
Data as the basis for targeting display advertising
- Every online user has a user data profile based on their usage over time. That profile forms the basis for digital advertising targeting
- Digital Data Profile contains cookies, Facebook ID, Google ID, device ID, location
Friday, March 9, 2018
[Search Engine Marketing] 04. Metrics
1. METRICS AND CAMPAIGN EVALUATION
- Translate your Marketing Objective into your top KPI. Depending on what action (conversion) you want your potential customers to perform, this is the Cost per Acquisition (CPA), Cost per Subscriber or Lead (CPL) or if you ‘just’ want traffic, you could go for Cost per Click (CPC)
- Your campaign ultimately is successful if you achieve your Marketing Objective at a cost below what you can afford to pay while keeping your desired level of profitability (ROI)
- The price per conversion (CPA/CPL) is driven by the conversion rate and the CPC
- The conversion rate can be optimized by improving and testing the quality of your landing page and aligning it with your ads
- The CPC can be optimized by improving the quality and relevance of your ads and landing page (Quality Score), which should, in turn, improve the CTR
- You can also lower the CPC by bidding for relevant keywords with less competition
- The number of impressions and the average position your ads receive are indicators of your Ad Rank relative to the competition
2. KEYWORD OPTIMIZATION STRATEGY
- Be specific and go long-tail (i.e. more specific and detailed keywords)
- Pause keywords with low CTR
- Use Match Types
- Add Negative Keywords
- Bundle closely related keywords in one Ad Group
3. STEPS TO CREATE AN A/B TEST
- Define one goal metric
- Identify one element of the ad that you want to test [Headline, Description, Call to Action, the promoted offer, Landing Page, URL Path, Ad Extensions, Ad Group Keywords, Location targeting, Time of the week/day (Advanced settings)]
- Create the different versions of your ads/ad groups (Run A/B test)
- Analyze your results
- Pause the lower performing version or continue testing by changing the next element
[Search Engine Marketing] 03. Ad Rank and Maximum CPC Bid
Let's learn about ad rank and quality score in Google Adwords.
1. AD Rank
- QS determined by
1. AD Rank
- Ad Placement = CPC BID x Quality Score
- Ad quality and relevance matters
- Quality Score and Ad Rank
- QS determined by
- Expected click-through rate(CTR)
- Landing page experience
- Ad Relevance
- Ad Formats
- Your conversion rate
- The unique value of one visit to your site: how much each new conversion is worth on average
- Customer Lifetime Value(CLV) / Average Order Value(AOV)
- ROAS(Return on Advertising Spend) = Total Conversion Value / Total Cost of Advertising
- Value of one visit = Conversion Rate * Average Money Spend by a Customer (conversion value/ AOL)
- Profit Margin = (Revenue - Cost of Goods Sold) / Revenue
- Calculate Max CPC Bid = Profit Margin * Unique Value of One Visit to Your Website
Tuesday, March 6, 2018
[Search Engine Marketing] 02. Text Ads @ Google
Ad extensions:
Enhance your Google Search Ads with additional, relevant information and give people reasons to check out your business.
No control which and when Google will show one or multiple extensions with your ad.
AdWords will select which extensions and how many appear in response to each individual search query on Google. Sometimes your ad will be shown with multiple extensions, sometimes without any.
There are four main components of a Text Ad:
- Two Headline Fields (Headline 1, Headline 2)
- Description Field
- Two Path Fields
- Final URL field
PC
- site links (up to 10)
- callouts (up to 4)
- structured snippets: highlight aspects of your business that fit into categories predefined by Google such as brands, destinations, styles or types.
- ratings

Mobile
- location
- call/ message
- price (carousel up to 8)
- app extensions (install button to app installation)
[Text Ad Best Practices (from Udacity)]
Highlight what makes you unique
When coming up with your headline, think of what makes you stand out from the competition. Your ad will likely be displayed among a few other ads that advertise products similar to yours. Go back to your Value Proposition you created earlier and make sure your potential customers know about what makes your product or service unique.
Include special offers or terms
If you offer free shipping, a money-guarantee, a sale or special offers (e.g. Buy one, get one free or 25% off everything), make sure to include that in your ad description. Calling attention to specific prices or promotions can help influence someone's decision to click on your ad.
Include numbers
Space is limited and numbers catch people’s attention very easily. Do you offer a fixed or low starting price or hourly rate that stands out? Or is your service available 24/7 or within 1 hour? Do you have 1,000 happy customers? Whatever number you can highlight to make your offering more attractive, consider to include it.
Use a call-to-action
Use your ad’s description lines to tell your customers what they can do on your site once they click your ad. Calls to action like a purchase, call today, order, browse, sign up, or get a quote make clear what the next steps are. Your call to action has to be specific to your offer and can’t include the word “click” (such as “click here” or “click now”).
Include testimonials
Did your product or service get a raving review by a trusted source? As we have seen earlier, you can include that review using the review extension, provided you can link to a source that is available online. If not, or if you want to guarantee that the endorsement shows up in your ad, you can include it in your ad description, e.g. “Best Value Flowers” - CBS News.
Create a mobile optimized experience
Especially if you are business with local stores or offices, people seeing your ads on mobile are more likely to want to know where you are or to call you. It’s a good idea to use location extensions and call extensions to show your location and phone number. Also, consider creating ads focusing on people on mobile devices, that link to the mobile-optimized version of your landing page.
Match your ad to your keywords
Try thinking like your customers and imagine what they might search for when seeking your product or services. Include their search terms as keywords in your ad text so that they can easily recognize that you offer exactly what they are searching for. Google also offers a feature called “keyword insertion” that dynamically updates your ad text to include one of your keywords that matches a customer's search terms. This is an advanced feature that requires some careful setup.
Match your ad to your landing page
When someone clicks on the link in your ad they should be taken to a landing page where they can do exactly what your ad promises without. The easier you make it for customers to find what they're looking for, the more likely they are to make a purchase. It’s also a good idea to have the main keywords from your ad prominently appear on your landing page.
Create at least two text ads per Ad Group
You can have more, but two ads to start will help you figure out which messaging resonates with searchers. When you have multiple text ads in an Ad Group, Google rotates the delivery because no more than one ad from your account can show at any one time. But Google, by default, runs the best ad. Said another way, once Google has sufficient data, Google optimizes for clicks. That means that Google shows the best performing ad in your ad group more often.
Do competitive research
To make your ad and offering stand out, it’s helpful to know what other ads potential customers will see next to yours. So, before you write your own ads, search for your most important keywords and have a look at what advertisers and ads you see and think about how you can stand out to your target audience. There are also helpful tools available (e.g. semrush.com) that help you identify your competitor’s major keywords and the ads they are currently running. These tools usually charge you, but often have a free trial version, which can be a great place to start.
[Avoid the most common mistakes]
In order to make sure all AdWords ads are of high quality, every ad must meet certain standards. Learn what those standards are and how to avoid common mistakes next!
Text Ad Common Mistakes
Once you save an ad, Google will evaluate the ad for approval and you will be notified when the ad is approved and ready to go. If you’ve done something Google doesn’t like in your ad, it will disapprove your ad and you have to edit it.
We will help you get your text ads approved by going over the most common mistakes. The majority of mistakes fall into two categories: mistakes with your ad’s copy, and mistakes with your ad’s URL.
Let’s start with your ad’s copy:
Avoid excessive or unconventional capitalization
You are free to capitalize words but stay away from excessive capitalization. For example, Google doesn’t allow ALL CAPS or capitalization within a word (such as SpEcIaL OfFeR).
Only use appropriate punctuation and symbols
You’ll also want to look out for excessive punctuation (“Buy Now!!!!”) and symbols (“Save $$$” or “flowers”). AdWords can disapprove ads with: multiple exclamation points (your ad description can only contain one exclamation point), an exclamation point in your ad's headline, repeated punctuation or symbols (e.g., [][][]), non-standard symbols like bullet points and vertical lines, or symbols or characters that don't match their true meaning, such as using the @-symbol next to the word ‘home’" to mean "at home."
Check your spacing
Make sure that you don’t use any extra spaces between letters or words in your ad’s text, such as f l o w e r s.
Don’t include phone numbers in your ad
Next, make sure you don’t include any phone numbers in your ad headline or description. Instead, use call extensions to include a prominent phone number in your ad. Google doesn’t allow phone numbers in the ad copy because it can’t track someone making a call (and thus can’t charge you for the action).
Make sure your ad copy is clear and describes what you're selling
Your ad can be disapproved if it uses gibberish or random letters, or if your ad’s text and URL don’t match, such as an ad for a clothing store that uses www.udacity.com as the URL.
Now let’s look at common mistakes related to your ad’s URL
Double-check your Display URL
Make sure that the display URL (the URL that people see in your ad) isn't mistyped, doesn't include "http" or "https", and doesn't use non-standard characters like exclamation points.
Make sure to use the same domain
Another common disapproval reason has to do with your URL’s domain. Every website has a domain, for example, udacity.com in udacity.com/courses. All ads within the same Ad Group need to have the same domain. Also, the domains for your ad’s display URL, final URL, and landing page URL need to have the same domain. In other words, the website listed in your ad needs to accurately show which website people will be taken to when they click your ad.
Enhance your Google Search Ads with additional, relevant information and give people reasons to check out your business.
- Manual: the extensions that you can manually set up on the account, campaign or ad level.
- Automatic: the extensions that Google will automatically generate.
No control which and when Google will show one or multiple extensions with your ad.
AdWords will select which extensions and how many appear in response to each individual search query on Google. Sometimes your ad will be shown with multiple extensions, sometimes without any.
There are four main components of a Text Ad:
- Two Headline Fields (Headline 1, Headline 2)
- Description Field
- Two Path Fields
- Final URL field
PC
- site links (up to 10)
- callouts (up to 4)
- structured snippets: highlight aspects of your business that fit into categories predefined by Google such as brands, destinations, styles or types.
- ratings

Mobile
- location
- call/ message
- price (carousel up to 8)
- app extensions (install button to app installation)
[Text Ad Best Practices (from Udacity)]
Highlight what makes you unique
When coming up with your headline, think of what makes you stand out from the competition. Your ad will likely be displayed among a few other ads that advertise products similar to yours. Go back to your Value Proposition you created earlier and make sure your potential customers know about what makes your product or service unique.
Include special offers or terms
If you offer free shipping, a money-guarantee, a sale or special offers (e.g. Buy one, get one free or 25% off everything), make sure to include that in your ad description. Calling attention to specific prices or promotions can help influence someone's decision to click on your ad.
Include numbers
Space is limited and numbers catch people’s attention very easily. Do you offer a fixed or low starting price or hourly rate that stands out? Or is your service available 24/7 or within 1 hour? Do you have 1,000 happy customers? Whatever number you can highlight to make your offering more attractive, consider to include it.
Use a call-to-action
Use your ad’s description lines to tell your customers what they can do on your site once they click your ad. Calls to action like a purchase, call today, order, browse, sign up, or get a quote make clear what the next steps are. Your call to action has to be specific to your offer and can’t include the word “click” (such as “click here” or “click now”).
Include testimonials
Did your product or service get a raving review by a trusted source? As we have seen earlier, you can include that review using the review extension, provided you can link to a source that is available online. If not, or if you want to guarantee that the endorsement shows up in your ad, you can include it in your ad description, e.g. “Best Value Flowers” - CBS News.
Create a mobile optimized experience
Especially if you are business with local stores or offices, people seeing your ads on mobile are more likely to want to know where you are or to call you. It’s a good idea to use location extensions and call extensions to show your location and phone number. Also, consider creating ads focusing on people on mobile devices, that link to the mobile-optimized version of your landing page.
Match your ad to your keywords
Try thinking like your customers and imagine what they might search for when seeking your product or services. Include their search terms as keywords in your ad text so that they can easily recognize that you offer exactly what they are searching for. Google also offers a feature called “keyword insertion” that dynamically updates your ad text to include one of your keywords that matches a customer's search terms. This is an advanced feature that requires some careful setup.
Match your ad to your landing page
When someone clicks on the link in your ad they should be taken to a landing page where they can do exactly what your ad promises without. The easier you make it for customers to find what they're looking for, the more likely they are to make a purchase. It’s also a good idea to have the main keywords from your ad prominently appear on your landing page.
Create at least two text ads per Ad Group
You can have more, but two ads to start will help you figure out which messaging resonates with searchers. When you have multiple text ads in an Ad Group, Google rotates the delivery because no more than one ad from your account can show at any one time. But Google, by default, runs the best ad. Said another way, once Google has sufficient data, Google optimizes for clicks. That means that Google shows the best performing ad in your ad group more often.
Do competitive research
To make your ad and offering stand out, it’s helpful to know what other ads potential customers will see next to yours. So, before you write your own ads, search for your most important keywords and have a look at what advertisers and ads you see and think about how you can stand out to your target audience. There are also helpful tools available (e.g. semrush.com) that help you identify your competitor’s major keywords and the ads they are currently running. These tools usually charge you, but often have a free trial version, which can be a great place to start.
[Avoid the most common mistakes]
In order to make sure all AdWords ads are of high quality, every ad must meet certain standards. Learn what those standards are and how to avoid common mistakes next!
Text Ad Common Mistakes
Once you save an ad, Google will evaluate the ad for approval and you will be notified when the ad is approved and ready to go. If you’ve done something Google doesn’t like in your ad, it will disapprove your ad and you have to edit it.
We will help you get your text ads approved by going over the most common mistakes. The majority of mistakes fall into two categories: mistakes with your ad’s copy, and mistakes with your ad’s URL.
Let’s start with your ad’s copy:
Avoid excessive or unconventional capitalization
You are free to capitalize words but stay away from excessive capitalization. For example, Google doesn’t allow ALL CAPS or capitalization within a word (such as SpEcIaL OfFeR).
Only use appropriate punctuation and symbols
You’ll also want to look out for excessive punctuation (“Buy Now!!!!”) and symbols (“Save $$$” or “flowers”). AdWords can disapprove ads with: multiple exclamation points (your ad description can only contain one exclamation point), an exclamation point in your ad's headline, repeated punctuation or symbols (e.g., [][][]), non-standard symbols like bullet points and vertical lines, or symbols or characters that don't match their true meaning, such as using the @-symbol next to the word ‘home’" to mean "at home."
Check your spacing
Make sure that you don’t use any extra spaces between letters or words in your ad’s text, such as f l o w e r s.
Don’t include phone numbers in your ad
Next, make sure you don’t include any phone numbers in your ad headline or description. Instead, use call extensions to include a prominent phone number in your ad. Google doesn’t allow phone numbers in the ad copy because it can’t track someone making a call (and thus can’t charge you for the action).
Make sure your ad copy is clear and describes what you're selling
Your ad can be disapproved if it uses gibberish or random letters, or if your ad’s text and URL don’t match, such as an ad for a clothing store that uses www.udacity.com as the URL.
Now let’s look at common mistakes related to your ad’s URL
Double-check your Display URL
Make sure that the display URL (the URL that people see in your ad) isn't mistyped, doesn't include "http" or "https", and doesn't use non-standard characters like exclamation points.
Make sure to use the same domain
Another common disapproval reason has to do with your URL’s domain. Every website has a domain, for example, udacity.com in udacity.com/courses. All ads within the same Ad Group need to have the same domain. Also, the domains for your ad’s display URL, final URL, and landing page URL need to have the same domain. In other words, the website listed in your ad needs to accurately show which website people will be taken to when they click your ad.
[Digital Marketing] How to Create Effective Social Media Content
Hub & Spokes Model
Hub: central to your content
Facebook content:
1. keep it short
2. use big, beautiful images
3. share exclusive content
4. respond to customers
5. tie your content to special events/ holidays
6. post for the right audience
7. posting on your page is about quality - not quantity
8. finally, avoid being overly promotional
- maybe change up your cover photos regularly
- use calls to action
- let customers know you're responsive
- use fun images
- use video
- run contests
- list job openings
- engage with quizzes
- custom tabs
- live videos through Facebook Live
Instagram Content:
1. encourage the audience to use name/hashtag
2. create contests
3. partner with influencers
4. re-gram photos
5. use creative hashtags
6. use compelling descriptions to accompany your pictures
7. use your bio space
Twitter Content:
1. keep it short
2. use visuals
3. incorporate hashtags
4. ask questions and run polls
5. curate and connect
6. seize the moment: live moments
7. match your tone to your brand & pay attention to trending hashtags
Youtube Content:
1. Post high-value content
Social Media Advertising Links
Facebook Pixel: https://www.facebook.com/business/help/952192354843755
All types of FB ads: https://www.facebook.com/business/learn/facebook-create-ad-basics/
Instagram Ads: https://www.facebook.com/business/help/976240832426180/
Twitter ads: https://business.twitter.com/en/help/campaign-setup/advertiser-card-specifications.html
Hub: central to your content
Facebook content:
1. keep it short
2. use big, beautiful images
3. share exclusive content
4. respond to customers
5. tie your content to special events/ holidays
6. post for the right audience
7. posting on your page is about quality - not quantity
8. finally, avoid being overly promotional
- maybe change up your cover photos regularly
- use calls to action
- let customers know you're responsive
- use fun images
- use video
- run contests
- list job openings
- engage with quizzes
- custom tabs
- live videos through Facebook Live
Instagram Content:
1. encourage the audience to use name/hashtag
2. create contests
3. partner with influencers
4. re-gram photos
5. use creative hashtags
6. use compelling descriptions to accompany your pictures
7. use your bio space
Twitter Content:
1. keep it short
2. use visuals
3. incorporate hashtags
4. ask questions and run polls
5. curate and connect
6. seize the moment: live moments
7. match your tone to your brand & pay attention to trending hashtags
Youtube Content:
1. Post high-value content
Social Media Advertising Links
Facebook Pixel: https://www.facebook.com/business/help/952192354843755
All types of FB ads: https://www.facebook.com/business/learn/facebook-create-ad-basics/
Instagram Ads: https://www.facebook.com/business/help/976240832426180/
Twitter ads: https://business.twitter.com/en/help/campaign-setup/advertiser-card-specifications.html
[Search Engine Marketing] 01. Keyword
When creating an ad campaign, finding the right keyword that could drive a lot of clicks is important.
Let's learn about finding the right keywords for your ad campaign.
Keyword List
- Brand Terms: Search ads of your own brand name increase 'clickability' by 25%.
ex) bamboohr/ bamboohr
- Generic Terms
ex) hr software/ hr payroll/ hr reporting
- Related Terms
ex) tools for hr manager/ managing hr more effectively/ tracking time off
- Competitor Terms
ex) zenefits/ zenefits software
Best Practices
1. Put yourself in your target persona's shoes
2. Add terms that reflect how people speak
3. Start broad, go specific
4. Include variations and synonyms
5. Include misspellings
6. Use tools like below:
- Google Trends
https://trends.google.com/trends/?geo=
- Google Keyword Planner
Long-tail keywords: longer and more specific keyword phrases
Combine keyword lists of both short & long tail keywords
Keyword Matching
- broad: your ad will show if a search query that matches your keywords whenever any word in your keyword phrase is searched, in any order.
+women's hats
- modified broad: plus sign(+) used; your ads will only appear on searches that contain the keywords that contain the +sign in them.
+women's + hats
- phrase: quotation marks("") used; your ad will appear for any search that includes the keyword phrase contained within the quotations in the exact order you've specified.
"leather women's hats"
- exact: your ad will appear only for the exact keyword phrase you've specified.
[LEATHER WOMEN'S HATS]
- negative: ensure your ad does not show for search queries containing certain words.
-men -
Let's learn about finding the right keywords for your ad campaign.
Keyword List
- Brand Terms: Search ads of your own brand name increase 'clickability' by 25%.
ex) bamboohr/ bamboohr
- Generic Terms
ex) hr software/ hr payroll/ hr reporting
- Related Terms
ex) tools for hr manager/ managing hr more effectively/ tracking time off
- Competitor Terms
ex) zenefits/ zenefits software
Best Practices
1. Put yourself in your target persona's shoes
2. Add terms that reflect how people speak
3. Start broad, go specific
4. Include variations and synonyms
5. Include misspellings
6. Use tools like below:
- Google Trends
https://trends.google.com/trends/?geo=
- Google Keyword Planner
Long-tail keywords: longer and more specific keyword phrases
Combine keyword lists of both short & long tail keywords
Keyword Matching
- broad: your ad will show if a search query that matches your keywords whenever any word in your keyword phrase is searched, in any order.
+women's hats
- modified broad: plus sign(+) used; your ads will only appear on searches that contain the keywords that contain the +sign in them.
+women's + hats
- phrase: quotation marks("") used; your ad will appear for any search that includes the keyword phrase contained within the quotations in the exact order you've specified.
"leather women's hats"
- exact: your ad will appear only for the exact keyword phrase you've specified.
[LEATHER WOMEN'S HATS]
- negative: ensure your ad does not show for search queries containing certain words.
-men -
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
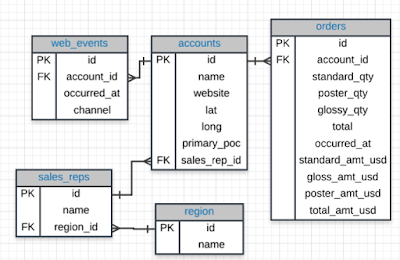
SQL Joins
Database Normalization: Are the tables storing logical groupings of the data? Can I make changes in a single location, rather than in...
-
I've started taking Digital Marketing Nanodegree at Udacity from Jan 2018. I'm going to write down what I've learned from the c...
-
Ad extensions: Enhance your Google Search Ads with additional, relevant information and give people reasons to check out your business. ...
-
1. Search Engine Optimization is Important Only 5.6% of clicks reach beyond the first page of search results. The first top 3 keywords ...















